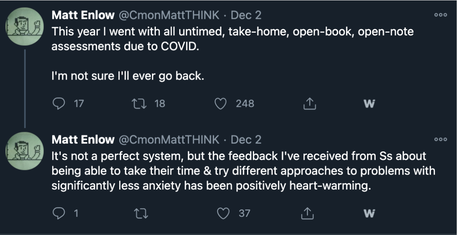
There are some hard questions that have been raised by educators about assessment:
- Is formative and summative assessment necessary during the pandemic?
- Do tests need to be proctored and/or timed?
- Can it really be considered an assessment if students are allowed to use notes and resources to craft their answers?
- Is it possible to move beyond assessing what students know to what students can do with their knowledge (apply, create, iterate, solve)?
- Are we measuring what we value?
- How can we use technology to assist in the creation of authentic and interactive assessments?
- Student Choice
2. Evidence of Mastery using Flipgrid. Example from Mike Mohammad (A secondary science teacher)
Create a Slide Deck and have each slide with a standard or learning target that students can submit a flipgrid response to. Check out the Bingo Card he created for students and the Slide Deck with Instructions. Students are presenting evidence and it’s in short snippets. If they are recording something in Flipgrid, it’s specific and not drawn out. They hit their target and move on to show evidence on the next standard in another Flipgrid submission. Everything is linked in a slide deck which makes it organized and easy for the teacher to assess. To make assessing the Flipgrid responses quick and efficient, organize students as individual topics (now called groups) in flipgrid. Greg Kulowiec explains this hack here.
3. Final Exams or Epic Finales by Anthony Crider
Could exam week become the best week of the year? Anthony Crider took the traditional exam and flipped it upside down to create a culminating experience at the end of the semester. After seeing a colleague tackle a final by asking one really good question, he set out to do the same thing.
“It took me longer to come up with that one good question than it did to pick 100 questions for my introductory astronomy class. I also trimmed the question down to be as short as possible, requiring students to “unpack” it even before answering it. As one student wrote to me afterward, “I think I spent as much time figuring out what the question was asking as I did answering the question.”
“The unspoken truth of education is that we don’t want students just to learn the material; we want them to want to learn the material. The final exam closes the book on a semester of learning. An epic finale primes the students to discuss the topic for weeks (or years) to come and to leave the classroom amid a bit more awesomeness than when they arrived.”
Developing an assessment that allows students to use their notes and the resources that are available to them on a daily basis. It is a question that can not be directly answered via Google because it requires analysis, interpretation, and application. The web will be a very helpful resource for students in collecting information related to these questions, but search engines will not lead to easy answers. Use Blooms Digital Taxonomy, adapted by Andrew Churches, to help craft questions that cause the learner to create, evaluate and analyze. Creating these questions will take time and practice. Get with your team and divide the learning targets that you’ll be accessing and use this template to help develop your questions.
5. ePortfolio - Collecting Evidence of Learning
A portfolio allows the assessment to shift and have the learner own the assessment process. John Spencer has a great collection of resources to help establish a portfolio process to collect evidence of learning and has included steps to take while curating a portfolio during distance learning.
How might the next assessment you develop look different? How would you lead teachers to re-think and change their assessments?













 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
